Wound Care in Miami, FL
Wounds on the feet are a common occurrence in people who have diabetes. This is because those with diabetes also tend to have peripheral neuropathy, a type of nerve damage that can cause loss of sensation in the lower limbs, and poor blood circulation. Any small cut, scrape, or sore on diabetic feet may go unnoticed because of a lack of sensation, while poor blood flow to the area can mean that any injury will heal slowly, poorly, or not at all. Left undetected and untreated, even small wounds can become diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs), which can become infected and lead to serious medical complications, up to and including amputation in the worst-case scenarios.
Causes of Diabetic Wounds
Some factors that contribute to the formation of wounds on the feet include wearing tightly fitted shoes, getting a pebble stuck in your shoe, or simply walking. What may appear to be just a small inconvenience such as a blister or callus can worsen over time, so it’s important to be safe and seek the attention of a professional. If you’ve developed a wound, it’s recommended that you try your best to keep the weight off of the area until you’re able to meet with a podiatrist.
Wounds should be taken care of immediately after discovery, as even the smallest of wounds can become infected if enough bacteria build up within the wound. To remove dirt, wounds should first be rinsed under running water only. Soap, hydrogen peroxide, or iodine can irritate the injury and should be avoided. To prevent infection, apply antibiotic ointment to the wound and cover it with a bandage. The bandage should be changed daily. The skin around the wound may be cleaned with soap.
To learn more about how to care for diabetic feet and prevent and treat foot wounds, please speak with a podiatrist.
Wound Prevention
In order to prevent these worst-case scenarios from occurring, people with diabetes should do everything they can to avoid wounds from developing in the first place. Managing their diabetes is essential. Keeping glucose levels under control can help reduce the risk of developing a wound.
Other ways to prevent wounds from developing include checking your feet daily for any injuries, washing and drying your feet daily, dressing for comfort and making sure your toes have enough space, and properly trimming your toenails straight across. You should also examine every part of your foot: the top of the feet, the bottom of the feet, the sides, the toenails, and in between the toes. A mirror can be used to aid in this daily inspection, if necessary. Things to look for include cuts, blisters, bruises, calluses, corns, sores, cracked skin, redness, bumps, lumps, ingrown toenails, puffy skin, tenderness, pain, or differences in temperature. Anything out of the ordinary should be reported to a podiatrist immediately.
When Diabetic Wounds Don’t Heal
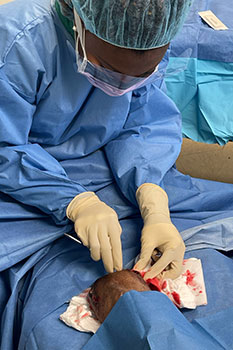
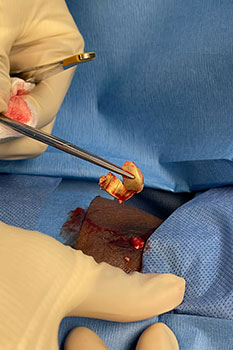
Wounds in a person with diabetes can be dangerous. A diabetic wound can heal slowly, not heal properly, or in some cases, never heal, making it an ulcer. Ulcers that are not healed promptly and properly have the potential of becoming infected and, sometimes, this infection may even spread to nearby tissue and bone, which is a serious health issue. An infection, and/or lack of blood flow can cause tissue to die, which is known as gangrene. Dead tissue must be surgically removed to prevent bacteria from entering and spreading through the bloodstream. This procedure is known as debridement. Early detection and intervention are extremely important in mitigating the risk to healthy tissue, and to prevent an amputation from becoming necessary.
Because wounds can lead to more severe complications, especially for those with diabetes, we recommend you speak with a podiatrist for professional guidance and a suggested plan for treatment.